
About the classical era of music
The classical music period was an era in music history which roughly spanned from 1730 to 1820. This period of music came after baroque music and was just before the Romantic period.
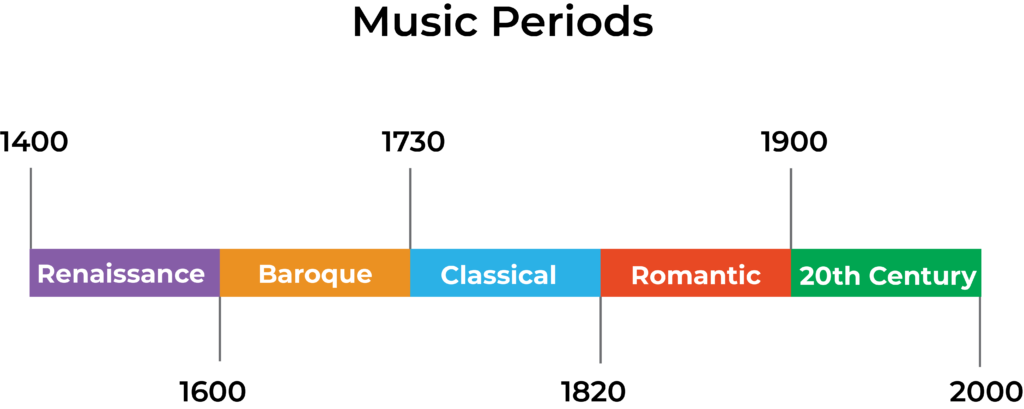
A brief history of the classical period
This era of time is titled ‘classical’ as the art and literature of the time had a huge interest and admiration for the classic artistic and literary heritage of Greece and Rome.
This time in history was also often labelled the age of enlightenment. This was a philosophical movement where people quite literally became enlightened on ideas about god, reason, nature and humanity. This then led to a revolution in art, philosophy and of course, music.
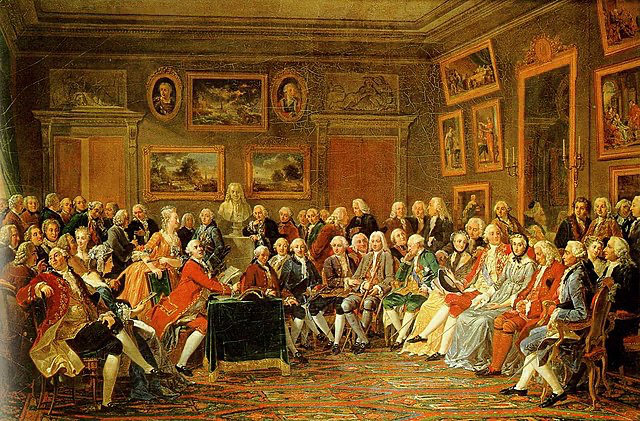
It is easy to see this stylistic movement within music as there is a clear move away from the baroque tradition of music written simply for the court or churches. Although music was still written for these musical settings, we now saw a rise in public concerts. This showed that the general feeling was that music should be written for the enjoyment of the general public as well.
What are the features of The Classical Music Period
1. Simplicity
Classical music had a bigger focus on simple melodies, simpler harmonies and much larger ensembles. This was very different to the elaborate and ornamented melodies of the baroque era. Melodies in the classical era often took their ideas from folk music and developed the composition of these by altering the tempo, dynamics and tonality. These ideas were then developed much further as music moved into the romantic era.
2. Clear musical forms
Similar to our point above, the musical forms used in classical music aimed to have order and structural clarity. The classical style was clear and musical compositions of the time reflected this with clear sections shown with traditional tonality, dynamics and other performance directions.
3. Increased accessibility
As we saw above, music now became much more accessible to the public with public concerts being much more common place. With this emphasis on public performance, composers were able to write slightly more freely as the new emphasis was on entertainment and enjoyment. We saw opera becoming more commonplace and with the enlightenment and the move away from traditional authority figures (such as the monarchy), opera began focusing on subjects that the average would enjoy. For example, Mozarts The Marriage of Figaro is about two servants that outsmart the ruling count and countess in a story about love, betrayal and fidelity.
Instruments of the Classical Music Period
During this time we saw the harpsichord being replaced with the piano. Piano music from then on slowly became much richer in tone. As the piano developed further it was able to play more sustained melodies and had much more dynamic contrast.
Orchestras during this time became slightly larger with clear sections of the orchestra being defined such as the string section and the woodwind section.
The woodwind section would generally consist of two flutes, two oboes, two clarinets and two bassoons, similar to what we see today. This would then sometimes be supplemented with other instruments such as the English horn (cor anglais), piccolo, contrabassoon etc.
The string section was eventually standardized within this era into what we know today, with the violin, viola, cello and double bass.
The percussion section would mostly just include the timpani, although in certain types of music you may see the bass drum, triangle, cymbals or tambourine being used.
The brass section was still not too developed, often just including the natural horn, natural trumpet, the sackbut (a precursor to the trombone) and the post horn.
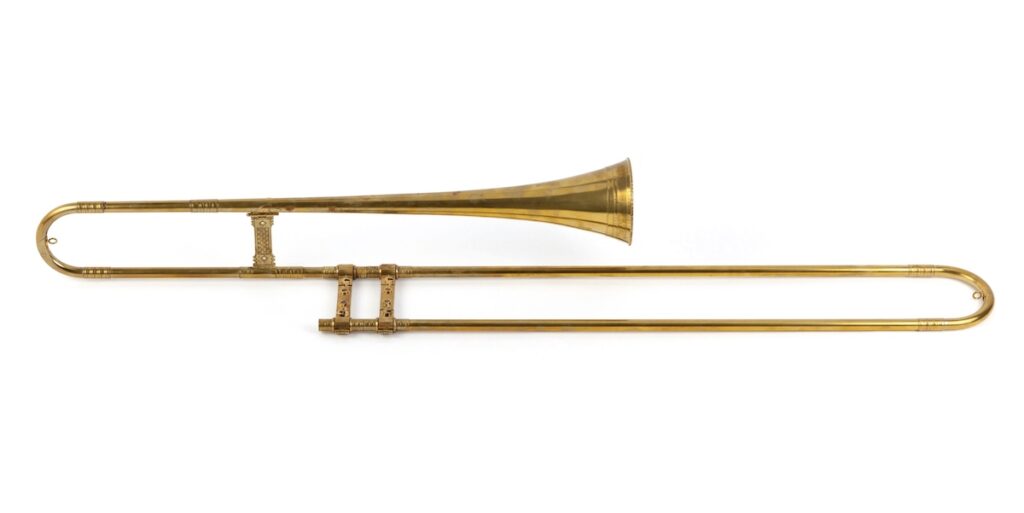
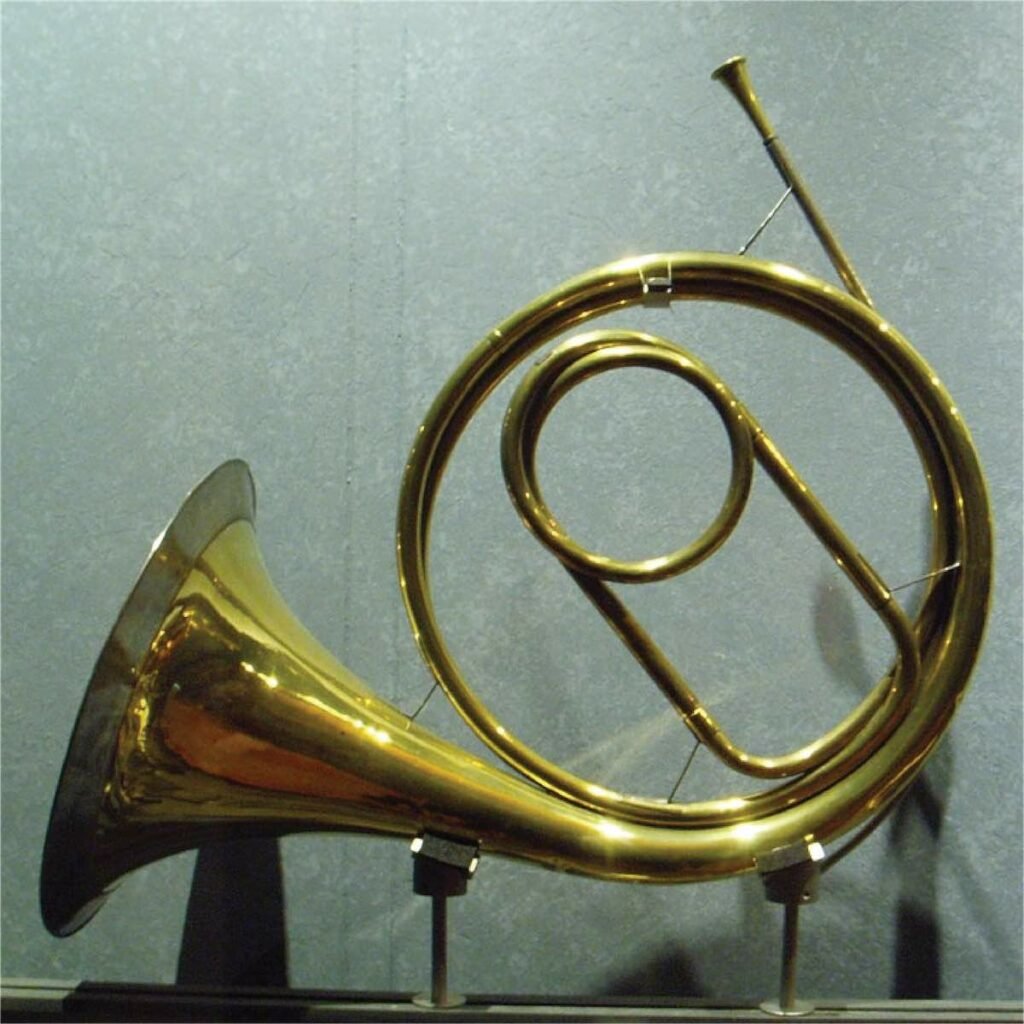
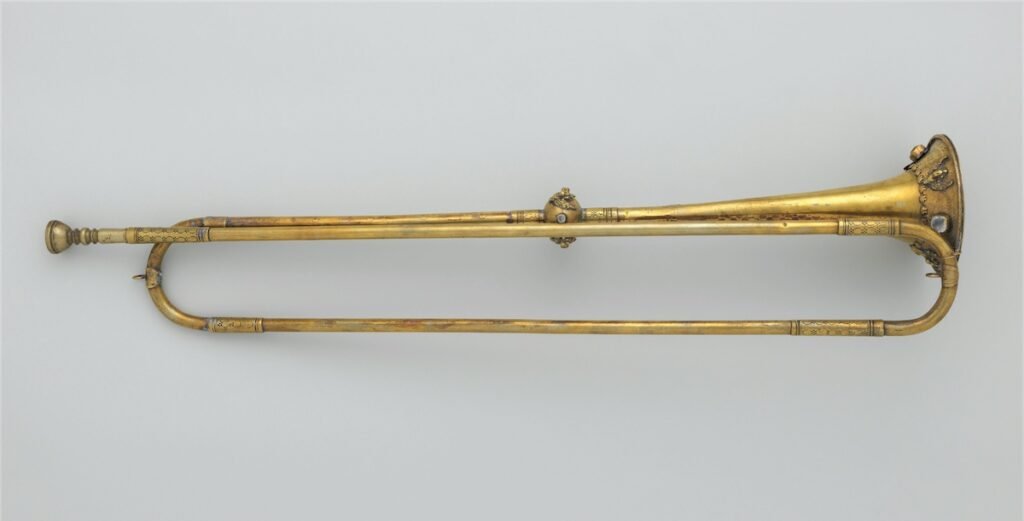



Common musical forms
Instrumental music became much more popular in the classical era, although choral music was still widely popular. The most common instrumental music forms in the classical era music were the:
- Sonata
- Trio
- String Quartets
- Quintets
- Symphony
- Concerto – this was now mostly written for virtuosi musicians to play on top of an orchestra.
- Serenades
- Divertimentos
Sonata form became possibly the most important form in this period though as it was used to help build many compositions such as symphonies and string quartets.
Classical period composers
Throughout this time, Vienna was where most of the composers came from and there was a particular group of composers that were often referred to as the viennese school. These composers were Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Franz Joseph Haydn, Franz Schubert and Ludwig Van Beethoven. There were of course many other famous classical music composers such as C.P.E Bach, Gluck, Salieri and Clementi but the viennese school of composers were considered the most influential.
Beethoven was right at the end of the classical era as some of his music is considered the beginning of the romantic era.
What’s next…?
- Learn more about the history of music with our guide to the Baroque Period.
