The Renaissance music period is one of the classical music periods from western history that spans from 1400 to the beginning of the sixteenth century. The Renaissance period was preceded by the medieval era and followed by the baroque era.
What does the word Renaissance mean?
The term ‘renaissance’ is a French term that literally means rebirth. It is used to describe the age of new discoveries and exploration between 1400-1600.
A Brief history of The Renaissance music Period
During this time there was huge political and social upheaval. The protestant reformation had a huge impact in this period. The protestant reformation was a religious revolution in which the Christian religion split into two, the Roman Catholic Church and the Protestant church.
The protestant revolution along with the catholic counter reformation in the sixteenth century liberalized some forms of art, but most profoundly church music and secular art music.
There was also an increase in humanistic thoughts which challenged the supremacy of the church. There was also a huge development in art and music as new techniques and styles were explored. A rebirth in the interest in ancient history, most notably ancient Greece and Ancient Rome also occurred at this time.

Much music from the renaissance music period was a cappella vocal music and from this an impressive polychoral style developed, as we moved further into the era. Music in the renaissance era had three distinct parts. The early renaissance, middle renaissance and late renaissance.
1. Early Renaissance Music
The early renaissance period centered around the Burgundian school. The Burgundian school was a group of composers led by the famous composer Guillaume Dufay. Early renaissance music closely followed the medieval period but composers now began to move away from syncopation and began using harmonic cadences.
Below you can hear Guillaume Dufay’s Ave Maris Stella. Notice the compositions links to the medieval period.
As the early renaissance period came to an end, the composers Johannes Ockegham and Jacob Obrecht started to include a lot more polyphony in their masses.
Below you can hear one of Franco-flemish composer, Johannes Ockegham’s, famous masses Missa Prolationum.
2. Middle Renaissance Music
The middle renaissance era started when the Roman Catholic Church began to discourage composer from polyphonic music. This led to composers embracing a much simpler form of harmony. One of the most famous composers from this middle renaissance era was Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina from the roman school. Palestrina introduced the beginnings of what we now call counterpoint.
Below you can hear an example of Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina’s pieces Stabat Mater.
3. Late Renaissance Music
The late renaissance era gave rise to a style called mannerism. This meant that music would begin to be embellished by with various things such as ornamentation, suspension and chromaticism. This would lead us into the heavily embellished music of the early baroque eras.
Orlando di Lasso was a late Franco-flemish renaissance composer who was highly regarded for his text painting, energetic rhythms and counterpoint.
Sacred and Secular Renaissance Music
When reading about the renaissance music period you will often see it referred to as either secular to sacred music. But what does this mean?
In basic form, sacred music is music based on religious topics and secular music is not, but let’s look at this in more detail.
Sacred Music
The early renaissance period was characterized by much sacred and religious music due to the dominance of the Catholic Church. As a result, we saw many polyphonic masses and latin motets. Modal counterpoint was the most common composition technique, probably due to it’s close relationship to liturgical plain chant from the preceding medieval era.
The renaissance music period was predominantly church music, but with the increase in humanistic thoughts we did see a move away from this. With the protestant reformation, music did start to be written for the protestant church, meaning a move away from the latin language and the structure of the catholic mass.
Common Music Forms Within Sacred Music
- Polyphonic Masses
- Sacred Motet
Secular Music
Secular music was very determined by the courts as they could finance and employ the renaissance musicians. Courts employed virtuoso performers
Some popular forms were the chanson, the madrigal and the German lied.
As the renaissance music period progressed, secular music pushed the boundaries paving the way for the major and minor tonal system we know now. functional harmony. Composers wanted to share more emotion in their music.
Secular renaissance music was mostly written for voice with instruments only being used to accompany. However, instrumental music did start to develop in its own right. Common secular forms were the fantasia and variations.
Common Secular Forms
- Secular Chanson
- Madrigal Dance MusicRenaissance Composers
Composers in the Renaissance Music Period
There are many famous renaissance composers who both wrote sacred and secular music. Early renaissance composers used features and musical styles from the Middle Ages, while later composers began to lead into the next era, the baroque era. Let’s take a look at some of the most famous composers from the renaissance era.

Guillaume Du Fay – 1397-1474 – Guillaume du fay was one of the earliest renaissance composers. Du Fay wrote much sacred music which was based on the Gregorian chant from the Middle Ages.
John Taverner – 1490-1545 – John Taverner was one of the most famous English renaissance composers and he wrote predominantly sacred music.
Thomas Tallis – 1505-1585 – Thomas Tallis was another very famous English renaissance composer. He actually composed music over the reigns of 4 monarchs. Henry VIII, Edward VI, Elizabeth I and Mary I. Tallis wrote mainly sacred music.
Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina – 1525 – 1594 – Palestrina was one of the most famous composers from the Roman School and is perhaps the most famous composer for his polyphonic style. vast vocal music from the Palestrina wrote a lot of sacred renaissance music, most particularly music for the voice.
William Byrd – 1543 – 1623 – William Byrd was one of the most famous English renaissance composers. Byrd was considered one of the first keyboard composers and you can find many of his piano works in My Ladye Nevells Book and the Parthenia.
Josquin des prez – 1440-1521 – Josquin des Prez was famous for writing both sacred and secular music. Josquin des Prez’s most famous musical forms are his masses and chansons.
Claudio Monteverdi – 1567 – 1643 – Monteverdi linked the renaissance music period to the baroque era, particularly with his famous operatic works. One of the most famous pieces Monteverdi wrote was his opera ‘Orfeo’.
Renaissance Music Period Instruments
The Renaissance music period was a time of huge developments and that included with musical instruments. Purely instrumental music was still a new concept in the sixteenth century, unlike what we see in modern music.
Below you can see some of the most common renaissance instruments as you can see many familiar modern instruments in this list but there was still a long way to go until these instruments would be like what we see today.
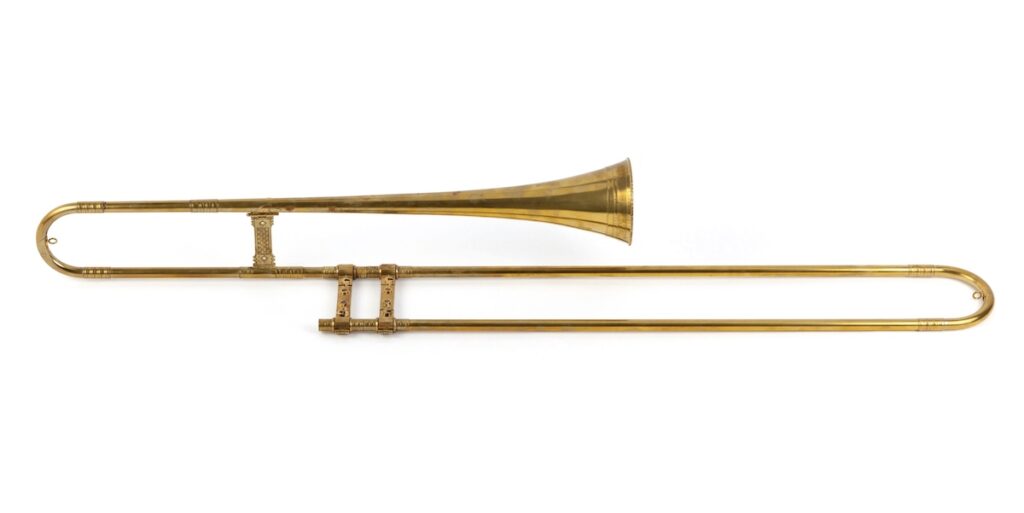
The ‘sackbut’ which is like a trombone.

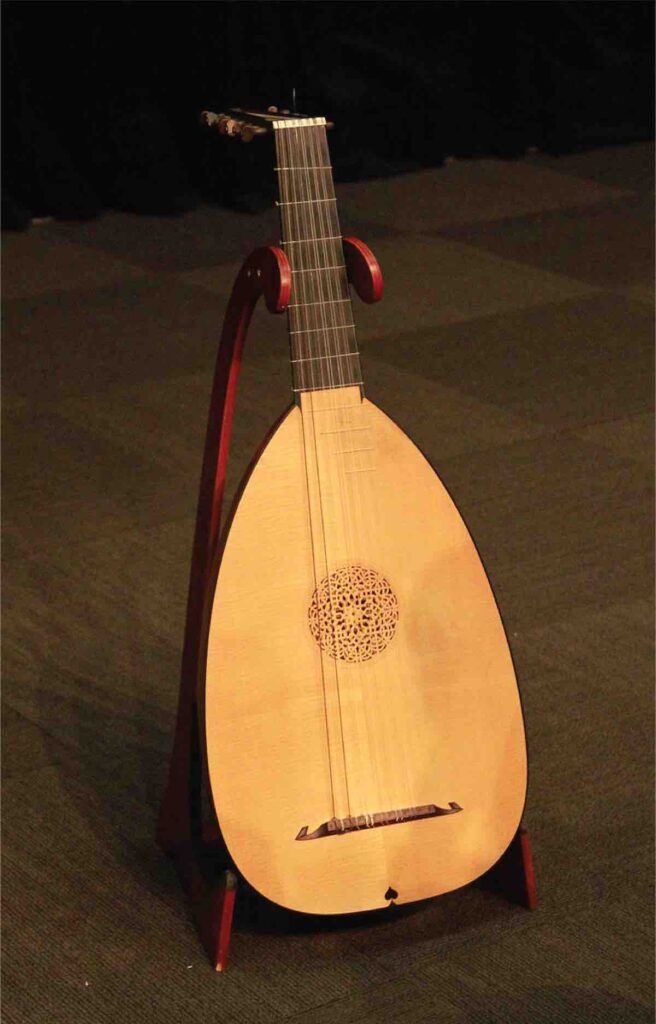
The lute

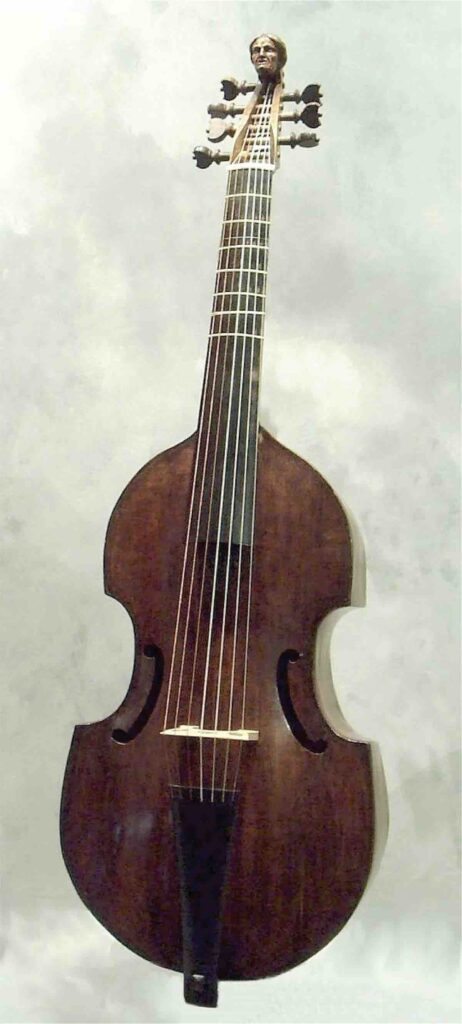
Viola da gamba

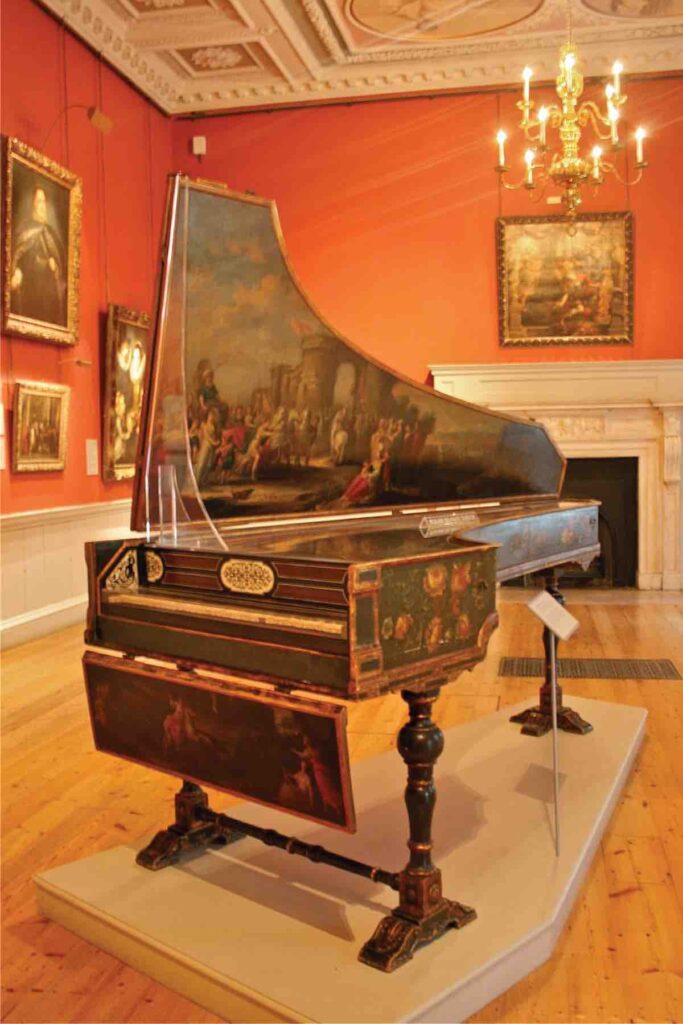
Harpsichord

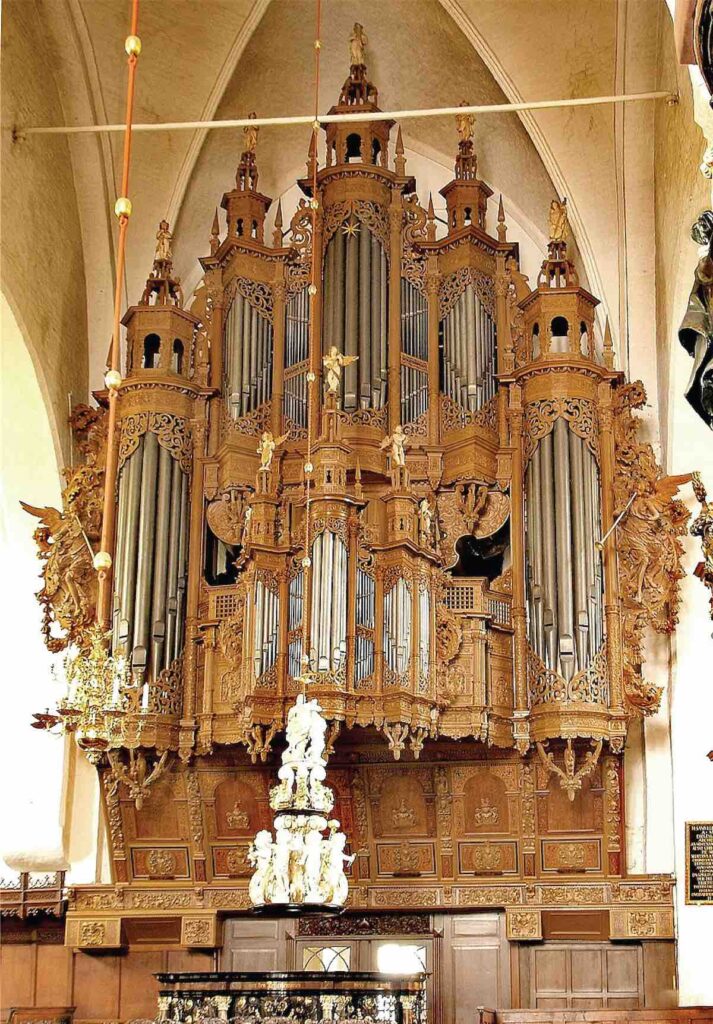
Organ

Main features of renaissance music
The renaissance music period saw a huge leap in sophistication from the medieval era. There were a few main features that characterized this era of western art music:
- Use of modes – Renaissance music used the ancient modal system, particularly in vocal music. However, in some newer styles such as the English madrigal and the Italian madrigal composers began to explore tonal music with an emphasis on cadences at the end of sections.
- Use of Polyphony – Renaissance music had a much richer texture than it’s preceding era of music. You would often hear four or more independent melodic parts.
- Risk taking – Renaissance music began pushing the boundaries of what came before. Renaissance music did not only include music for voice, but with the invention of more musical instruments a greater focus on instrumental music became prevalent.
- Renaissance music was generally characterised by two main sections, sacred renaissance music and secular renaissance music. Sacred music was written for the church and secular music written for the courts.
Renaissance sheet music
The printing press was invented in c.1400 and this had a huge impact on the western world, particularly the music world! As it became easier to copy music it became more common for people to have sheet music.
During the Renaissance music period, sheet music was similar to how we see it today. With the invention of the printing press there was a much stronger feeling that musical ideas should have a unifying musical language to make it easy to read.

However, there are some important differences:
- No bar lines
- Mostly used semibreves
- Only single lines or polyphony shown on music, no score showing all parts
The distribution of sheet music now meant different techniques could be studied by all.
What next…?
The next thing to look at will be the other periods of music!
- The Baroque era
- The Classical era
- The Romantic era
- The 20th century era
