The Romantic period closely follows the classical period of music. The romantic era was known for its intense passion and its move away from the rigid structures of classical music. Music in the romantic period sought to move closer to other art forms such as art poetry, literature and nature. Romantic music was closely related to the concept of Romanticism and we will look at this as we go through this post.
About the Romantic Music Period
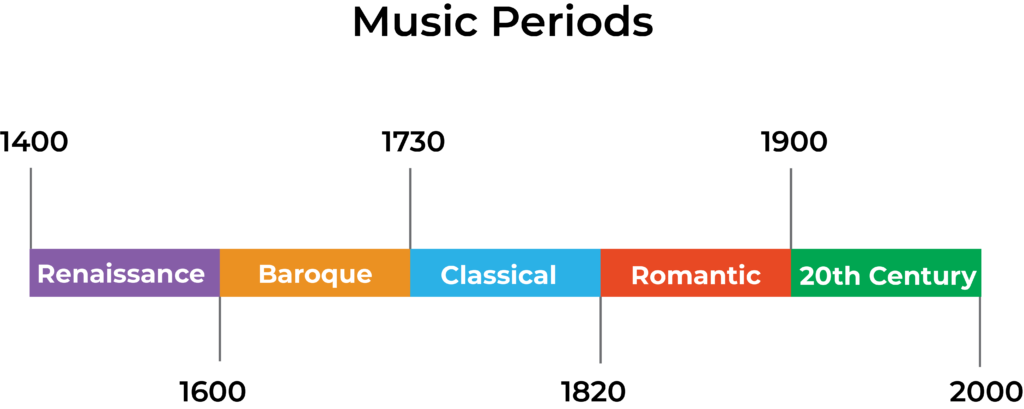
The Romantic period roughly began in 1830 and finished around 1900. It was the next period of music following the classical era and later the 20th century music. Romantic composers in the 19th century found inspiration from the natural world, mystic and supernatural ideas, poetry, romantic art and more. There was a huge move away from the rigid structure and musical forms of the classical era and a move towards human expression.
Romantic music was closely linked to what was going on at the time and this was romanticism.
Key Romanticism Art Characteristics: A Romanticism Definition
Romanticism was the intellectual, artistic and literary movement happening in western culture. This was towards the end of the 18th century/early 19th century, mostly based in Europe. It is sometimes referred to as the European romantic movement.
Romanticism began in 1770 (roughly) at the same time as the French Revolution and as a reaction to the disillusionment of the Industrial Revolution and the disillusionment of the enlightenment values. Romantic music was heavily influenced by the powerful feelings of the time and was mostly inspired by non-musical themes such as poetry, literature, nature, a revived historical appreciation and romantic ideas.
This movement in history emphasized the intense emotion of the human mind such as fear, horror, terror and awe.
Romanticism could be seen in all art forms such as literature, art, architecture and music. Romantic literature had a very particular literary style whether this be romantic poetry, gothic fiction, prose work or blank verse all of these were celebrating nature, individuality, spirituality and the great spectrum of emotions that humans feel. Romantic poetry in particular would explore the physical landscape with long poems exploring this topic and expressing underlying emotional challenges.

The visual arts also become extremely important during the romantic movement. Romantic artists were deeply interested in topics such as the power of nature, human emotion and the expression of feelings just as we have seen in literature. Many paintings from the romantic style would be landscape painting or history painting, depicting scenes from ancient history.

Romantic architecture mostly expressed itself through imitating older architectural styles and medieval ideas.

Romanticism prioritised the imagination of the artist and moved away from the artificial rules put in place from the previous periods. Instead expressing the full scope of human emotion was put at the forefront.
The Transition from the Classical Era to the Romantic Era
The composer that really began and bridged the gap between the classical and romantic era was Ludwig Van Beethoven (1770-1827).
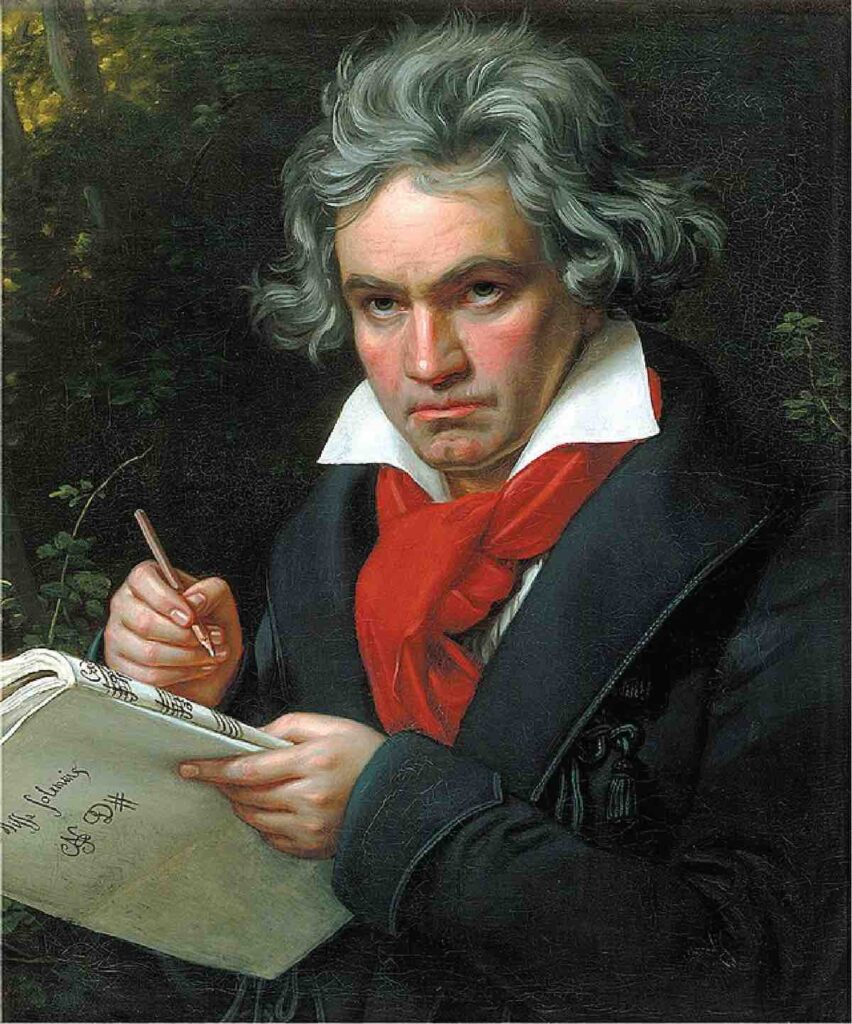

Beethoven began writing much more expansive and ambitious works that challenged and moved away from the strict rules created by composers such as Mozart and Haydn.
Another innovation he had was to begin writing programmatic music. Programme music is music that suggests non-musical elements such as depicting nature, literature, ancient ideas and more.
Ludwig Van Beethoven’s Symphony 6 really shows this. Symphony 6 is also known as ‘the pastoral symphony’ as it depicts rural life. Listen out for the imitation bird calls!
Key Features of the Romantic Period
The Romantic Music Period was a step away from the classical era, it became much more autobiographical and composers wanted to express the full spectrum of human emotions. Expressing emotions became much more important than sticking to the rigid musical forms and stuctures of the previous periods of music.
Pieces were much harder than we had previously seen, with more complex and longer melodies and programmatic elements. Romantic music had much more unpredictable chord sequences with cadences that end in unexpected ways.
The virtuosi was born during this era as well. With melody lines becoming much harder, the demand on musicians musical techniques increased and with this came the need for especially skilled musicians called virtuosi!

Instruments were also greatly improved during this time, allowing for much more expression and a much larger dynamic range. We also saw the expansion in the orchestra allowing for a much larger range in pitch. This expansion in the range of pitch was also seen a lot in piano music.
To add to the expression in romantic music we also saw a huge use of rubato. Rubato was literally a freedom of time.
We also saw many composers coming back to their roots with much more nationalistic music. Some examples are:
Jean Sibelius’s Finlandia – this has been interpreted to show a protest against the censorship in Finland by the Russian empire
Smetana wrote music pushing for Czech independence
Chopin celebrated music from his traditional folk music of Poland
Musical Forms
The Romantic movement gave rise to many new musical forms. These included programme music, tone poems, the nocturne, arabesque, rhapsody and concert overture.
Programme music
Programme music is instrumental music that carries a non-musical meaning. Essentially a programme of a literary idea, description of nature, an autobiographical element or an ancient legend.
Camille Saint-Saëns’ ‘ The Carnival of the Animals’ contains 14 movements, each of which represents a different animal. Below is movement 1 titles ‘March of the Lions.
Tone Poems
A tone poem (sometimes called a symphonic poem) is a single movement orchestral work around a particular theme. It will be written to evoke the content of a poem, short story, novel, the natural world, romantic painting or some other non musical source.
Antonín Dvořák composed five symphonic poems throughout his career. ‘The Noon Witch’ is inspired by the poem Polednice, written by Karel Jaromir Erben.
Nocturne
A nocturne is another musical composition inspired by non musical ideas. But these ideas are specifically about the night! Frederic Chopin wrote many nocturnes, take a listen to the below example in G minor.
Arabesque
An arabesque is a highly ornamented piece of music that uses melodies to create the atmosphere of Arabic architecture. An example of this is Claude Debussy’s Deux Arabesques. This was composed in 1888 and 1891.
Rhapsody
A rhapsody is another one movement work that has episodes which feature many contrasts in mood, color and tonality. Despite this it is still free flowing in its structure. A great example of this is from Johannes Brahms. Take a listen to his Rhapsody in E-flat major for solo piano.
Concert Overture
The concert overture was a one movement work to introduce a romantic opera, oratorio or ballet or as an independent work based on one of these genres. Ludwig Van Beethoven and Felix Mendelssohn were particularly fond of this musical form. Take a listen below to Mendelssohn’s The Hebrides.
All of these new forms allowed composers to explore many non musical ideas. It was a way to express emotions and feelings.
Vocal music in romantic period
Vocal music also expanded during the romantic period, and we started to see a new form called the lieder. The lieder were most often composed using German Poetry.
Schubert wrote many lieder’s.
The romantic period also saw composers putting together song Cycles. A song cycle literally involved composers grouping together songs with similar themes. Franz Schubert wrote two long song cycles, Winter’s Journey and The Beautiful Miller’s Daughter. Learn more about Winter’s Journey below.
Opera – Golden Era
Perhaps one of the most famous genres that really took off in the romantic period was the opera! Although opera was around from the baroque period, opera really took off in the 19th century. Some operas around this time would have upwards of 100 performers with huge orchestras and large casts. There were two big schools of opera, namely the Italian romantic opera and German romantic opera. Take a listen to Giuseppe Verdi’s La Traviata and Richard Wagners Tristan und Isolde.
Virtuosi players
We also saw a huge rise in virtuosi performers in the romantic period. These virtuosi musicians were highly skilled performers that would be able to play extremely challenging music. Niccolo Paganini was a famous virtuosic violinist and one of the first virtuosi.
Developments in Musical Instruments and the expansion of the orchestra
During the romantic era we also saw a huge expansion of the orchestra. We now saw a much larger string section, larger woodwind section, brass section and percussion section!

Composers of the Romantic Era
The romantic movement gave rise to many new composers, particularly in European countries.
Some of the most famous composers from this era are:
- Ludwig van Beethoven (1770-1827) – Germany
- Felix Mendelssohn (1809-1847) – Germany
- Robert Schumann (1810-1856) – Germany
- Frederic Chopin (1810-1849) – Poland
- Richard Wagner (1813-1883) – Germany
- Giuseppe Verdi (1813-1901) – Italy
- Johannes Brahms (1833-1897) – Germany
- Pyotr llyich Tchaikovsky (1840-1893) – Russia
- Jean Sibelius (1865-1957) – Finland
