Transposition is essential skill for any aspiring musician. At their heart of it, transposition allows you to alter music so that it can be played on different instruments or in different ranges of pitch.
So let’s take a dive into how to transpose down a perfect 4th. This is both for music theory students and for musicians seeking to understand the concept of transposition.
Need to transpose using another interval; check out all our transposition guides here.
What Is A Perfect 4th?
A perfect 4th interval is created when we move from the 1st degree of the scale to the 4th degree to the scale. This interval is called a ‘perfect’ third because it is the 3rd note of the major scale.
Another way of thinking about a perfect 4th is that it is 5 half-steps above the lower note. More perfect 4th examples here.
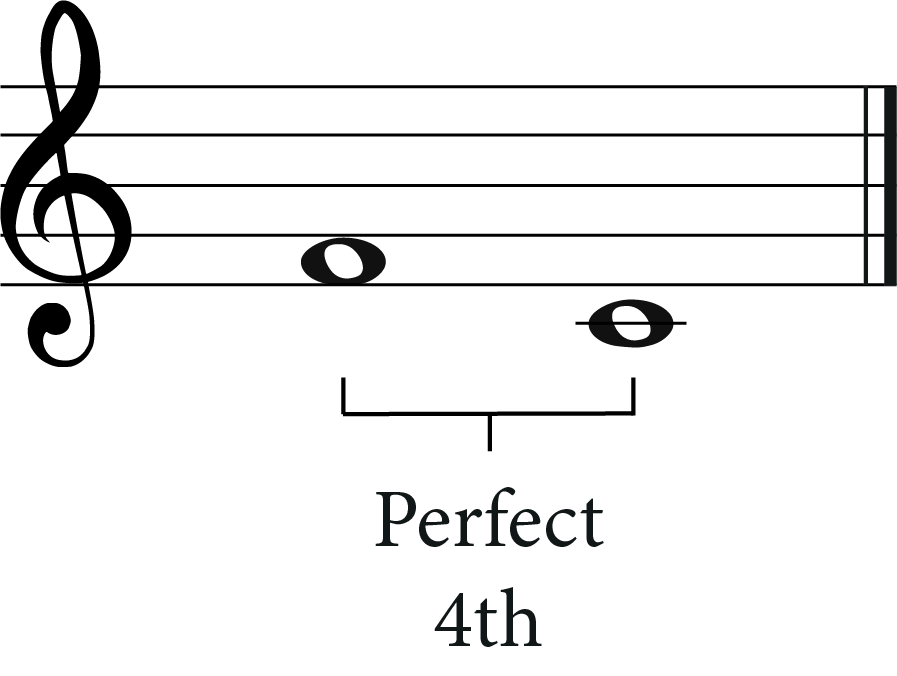
It’s worth remembering that 2nd, 3rd, 6th and 7th intervals can also be major or minor, whereas 4th and 5th intervals are described as ‘perfect’.
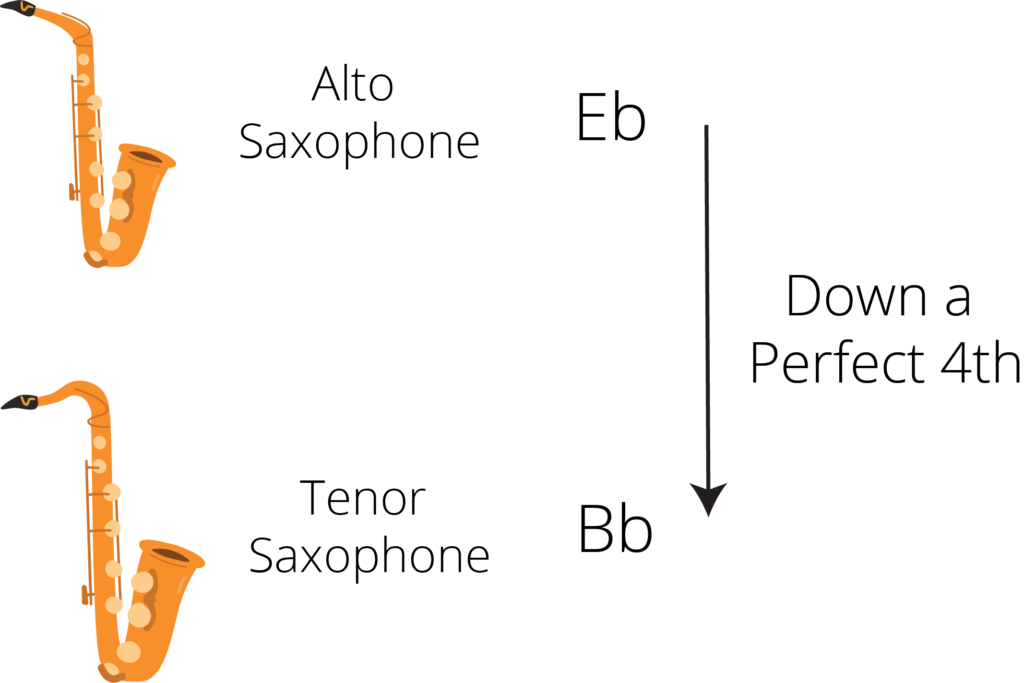
Why transpose Down a Perfect 4th?
One of the most common uses of this type of transposition is moving from the tenor saxophone to the alto saxophone.
The alto is in Bb and the tenor is in Eb, so to rewrite music from the alto to the tenor we can transpose down a perfect 4th. This will mean that we can play a tenor saxophone piece on the alto saxophone.
In the same way we could transpose a tenor piece for the alto sax. This would involve transposing the piece up a perfect 4th.
How To Transpose Down A Perfect 4th
This method has three steps:
- Transpose the key signature down a perfect 4th
- Move all the notes down a 4th
- Deal with the accidentals
(If you thought we could transpose each note one at a time, click here to see why NOT to do this)
Let’s try an example. Have a look at the melody below and let’s transpose it down a perfect 4th.
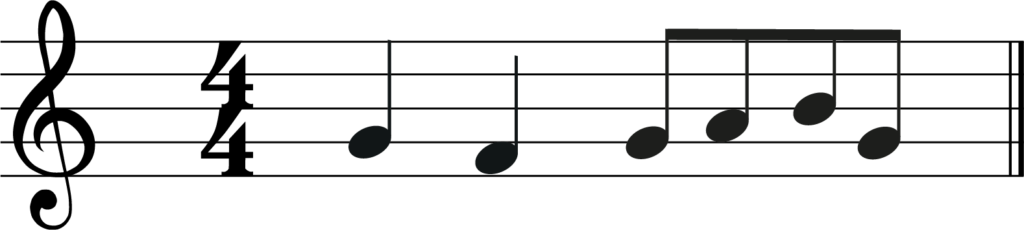
Step 1- Transpose The Key Signature
First, let’s transpose the key signature. Our melody is the key of C major, so what is a perfect 4th below C natural?
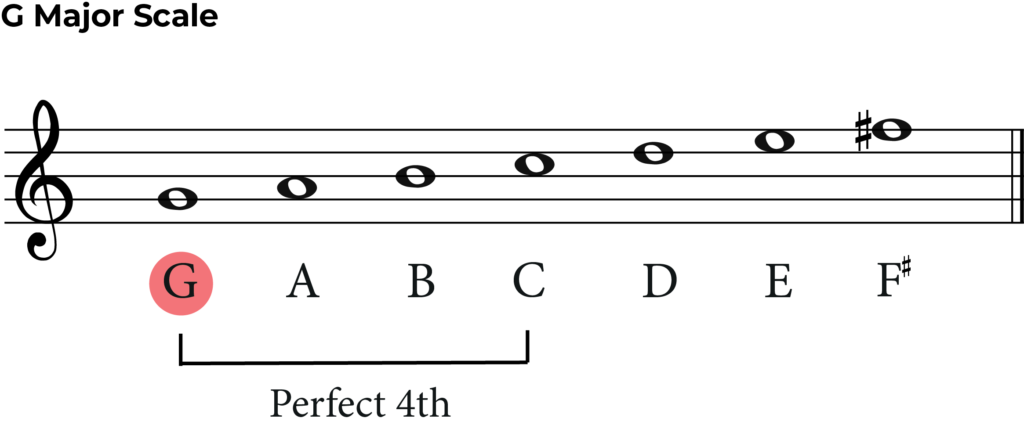
As you can see above, a perfect 4th below C is G natural. This means that we now need to put the key signature of G major at the start of our melody.
The key signature of G major has one sharp – F#.
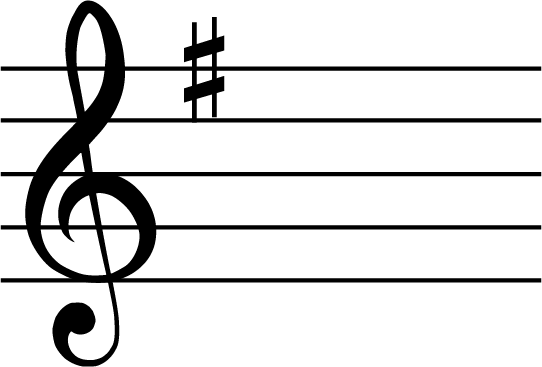
Here it is in our melody.
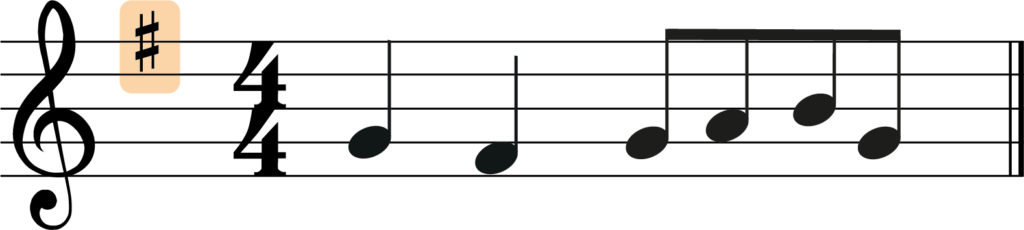
- If you are unclear on your key signatures, please make sure you are familiar with your Circle of Fifths.
Step 2- Move The Notes Down A 4th
Once you have changed your key signature, we then need to follow this with moving all the notes in the melody down a 4th. As with all intervals we include the starting note, so effectively this means moving the notes down three times.
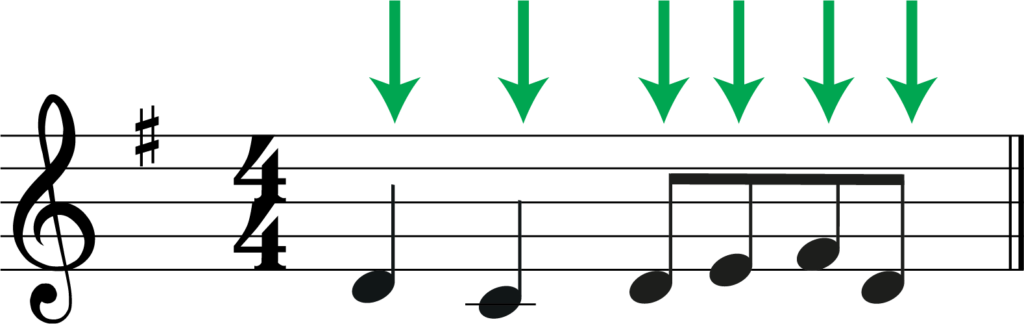
And we have our transposed melody! Below is the original melody with the tranposition underneath.

There are no accidentals in this melody so no need for step 3 this time.
Example 2
What key is our melody in below?

That’s correct, we are in B flat Major!
Step 1- Transpose The Key Signature
First let’s transpose the key signature. Can you transpose down a perfect 4th from Bb?
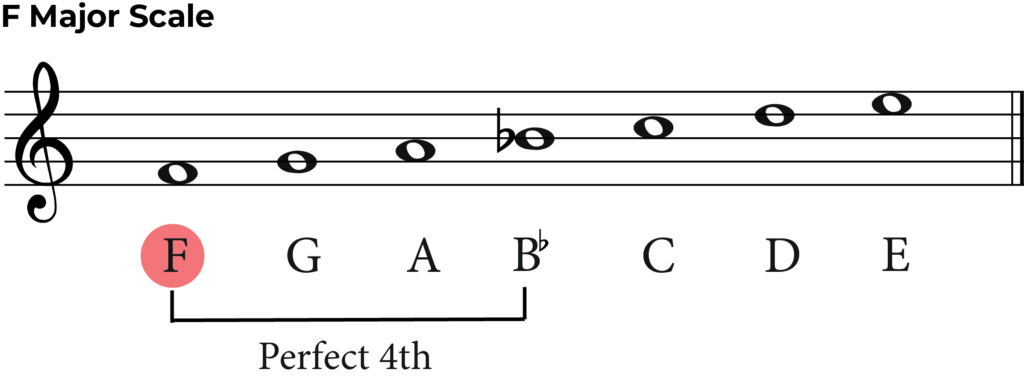
B flat is the 4th note of the F major scale, so F is a perfect 4th below Bb. This means we now need the key signature of F major. F major has one flats – Bb.
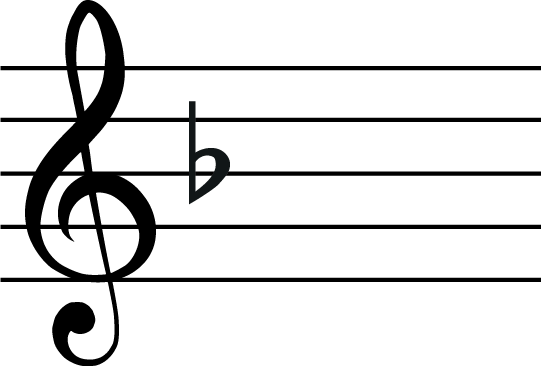
Here is the new key signature at the start of our melody.

Step 2- Move The Notes Down A 4th
Now we have changed the key signature, simply move all of your notes down a 4th.
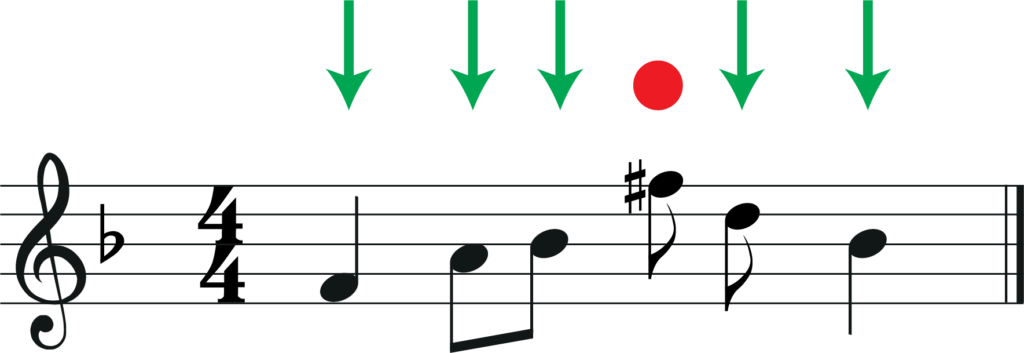
As you can see, we have not moved the F sharp note yet. This is because it is not in the notes of the original key signature and so will need to be treated differently.
Step 3- Accidentals
In our original melody we have a F#. This note is not in the key of Bb major and so it will not be transposed correctly by the first 2 steps.
To transpose this note we treat it on its own. We can ask: what is a perfect 4th below F#?
The easiest method in this case would be to lower the F# a half-step to an F. Finding a Perfect 4th below F is much easier: it is C natural. Then we raise the C up a half-step to correct it to C sharp.

Can We Transpose One Note At A Time?
This is the slowest method of transposing, but it works! Here we are going to move each note down a perfect 4th interval to create our transposed melody.

Remember that for each different note we need to count down a 4th in a different key. Because of this it can be way easier to make mistakes. You will also need to look at your notes to figure out the key signature for your new melody, otherwise you may have a lot of accidentals to read!
What’s Next….?
- Learn how to transpose DOWN a perfect 4th.
- Learn how to transpose by another interval.
- Learn more about intervals with our complete guide.
FAQs
How Can I Transpose Sheet Music Up A Perfect 4th Automatically?
There are a variety of apps that can transpose sheet music such as Sibelius and Musescore.
What About Transposing A Piece In A Minor Key Down A Perfect 4th?
If you have a piece in a minor key then transposition works much the same. Remember that a minor piece will be transposed into another minor key even through we are moving it down a perfect 4th. (Similarly a piece with a major key signature will be transposed to another major key).
For example, a piece in A natural minor would be transposed into the key of E minor (one sharp – F#). This is because E natural is the 4th note of the A major scale and the A Minor scale.
In a way, it’s easier to think of the original key signature without the major/minor label. If the piece is in A minor, just start with the note A natural and transpose from there. Just remember pieces do NOT change whether they are major or minor by transposing them.
Important- beware of accidentals as these need to be treated independently. Scales such as the harmonic minor and melodic minor use additional accidental outside the key signature.
