Each minor scale can be used to create chords in that key. These can be used to create chord progressions that underpin melodies and will allow you to create pieces in any key you like.
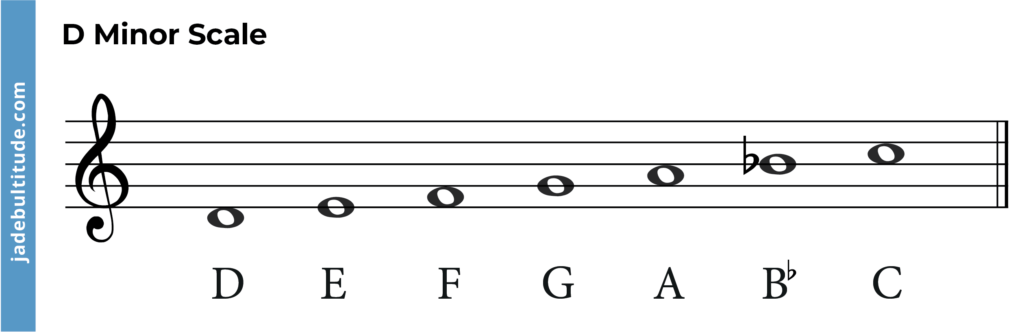
Chords in D Minor are created from the D Minor scale. The notes in the D natural minor scale are shown below along with the degree of the scale.
- D – 1, Tonic
- E – 2, supertonic
- F – 3, mediant
- G – 4, subdominant
- A – 5, dominant
- Bb – 6, submediant
- C – 7, leading note
You may notice that these notes are the same as the F Major scale which also has one flat. This is because F Major is the relative major key to D Minor.
Chords in D Minor
As with all keys, we can create chords on each note of the D minor scale. Below you can see the chords in D minor and their individual notes. Notice that we have a B flat in some of the chords. This is because D natural minor has one flat in its key signature.
Each chord is also called a triad and consists of the root note, the 3rd above and the 5th above (in the scale). If we use this idea for every note of the scale, we get all 7 chords in the key of D minor.
Here are the chords in D minor:
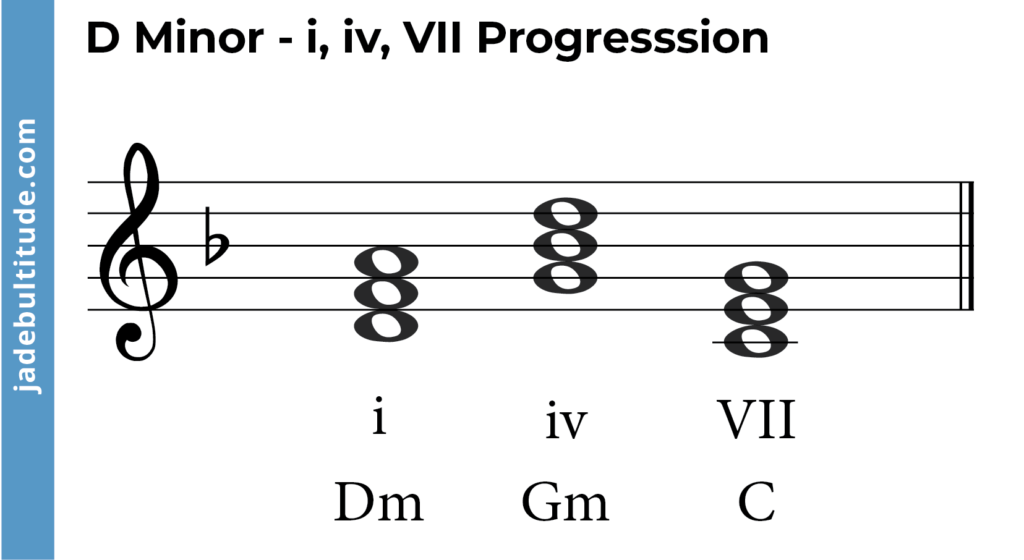
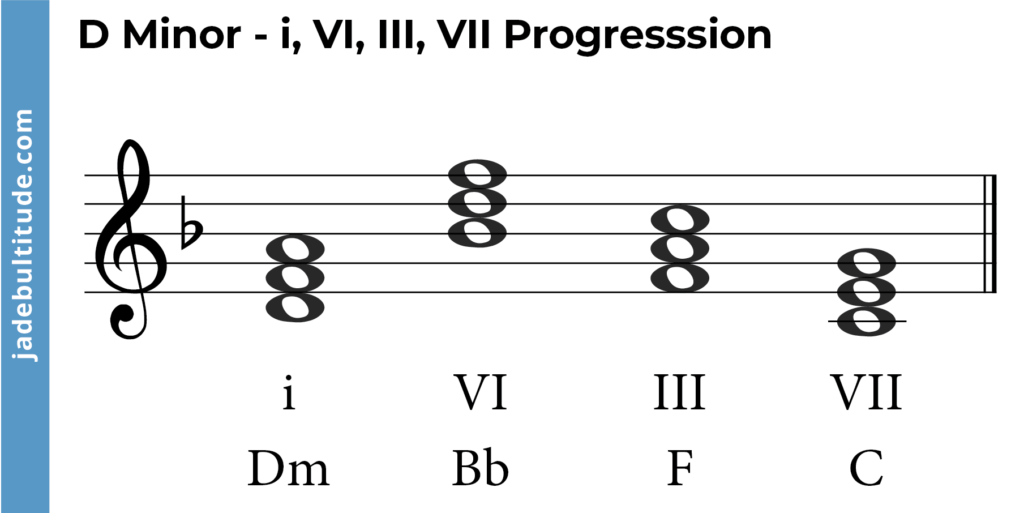
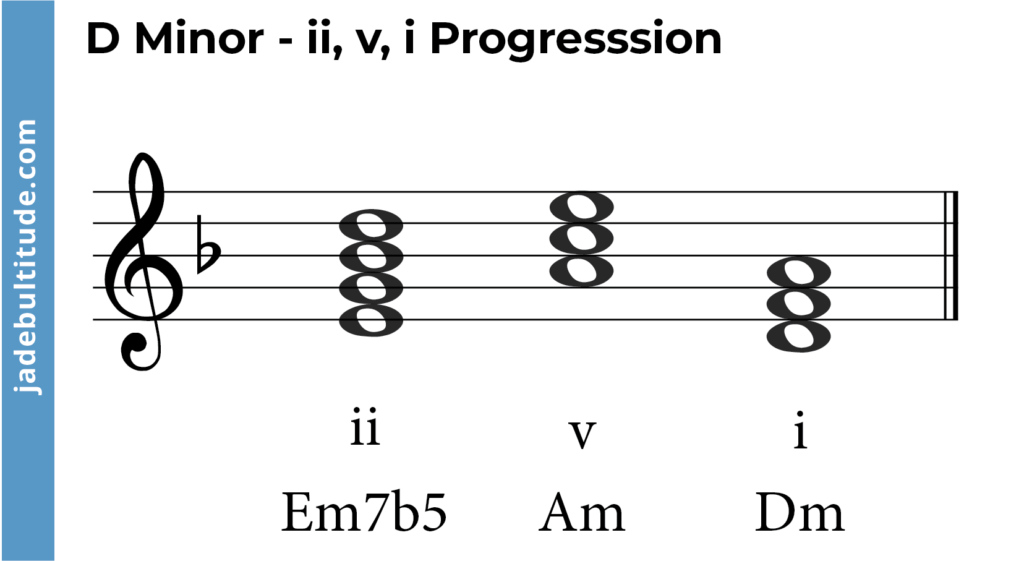
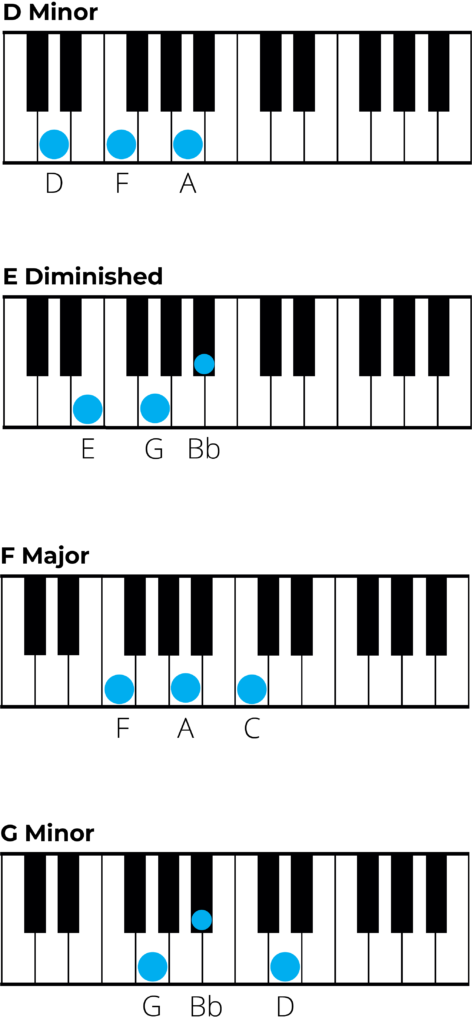
- i – D Minor: D – F – A
- ii° – E diminished: E – G – Bb
- III – F major: F – A – C
- iv – G minor: G – Bb – D
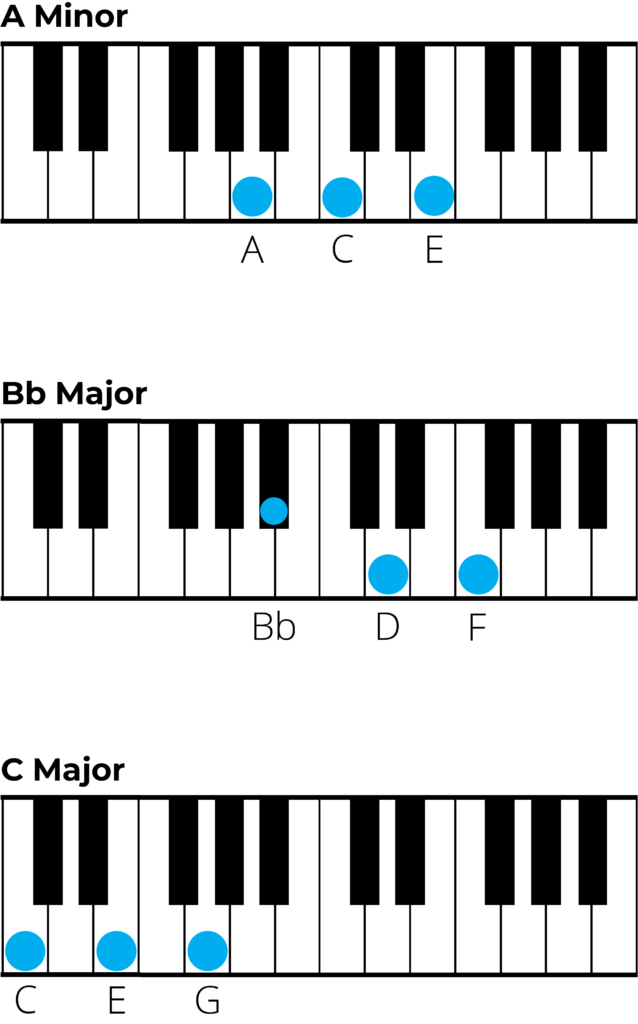
- v – A minor: A – C – E
- VI – Bb major: Bb – D – F
- VII – C major: C – E – G
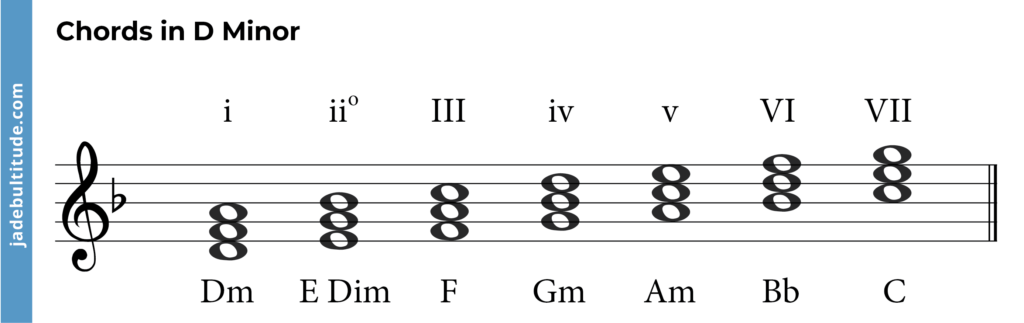
As you can see, we can label each chord according to the root note and using Roman numerals. Learn more about Roman numeral chord labelling. For a lightning quick summary, upper case numerals are MAJOR, lower case are MINOR and the little circle means DIMINISHED.
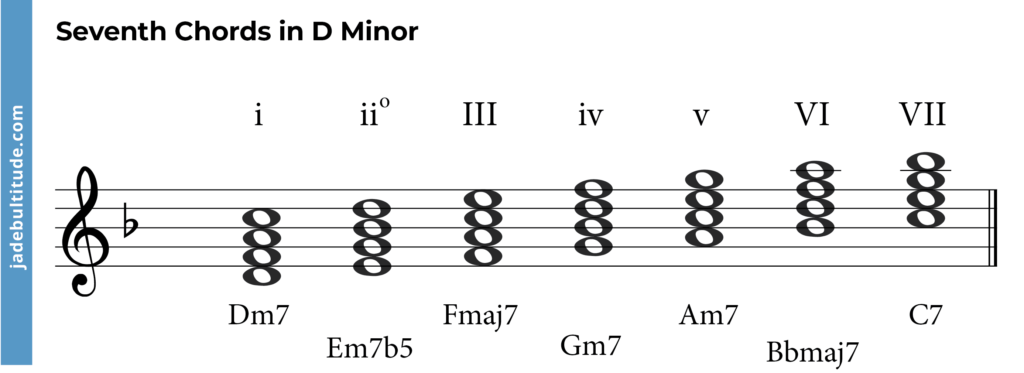
Seventh Chords In D Minor
Notice that all of the chords labelled above are three note chords, otherwise known as triads. It is also possible to make four note chords on these different scale notes. These would be called seventh chords. The first note of the chord will stay the same but you will simply add an additional note, a seventh above the tonic. Take a look at the example below:
- i – D minor seventh: D – F – A – C
- ii° – E minor seventh flat five: E – G – Bb – D
- III – F major seventh: F – A – C – E
- iv – G minor seventh: G – Bb – D – F
- v – A minor seventh: A – C – E – G
- VI – Bb major seventh: Bb – D – F – A
- VII – C dominant seventh: C – E – G – Bb
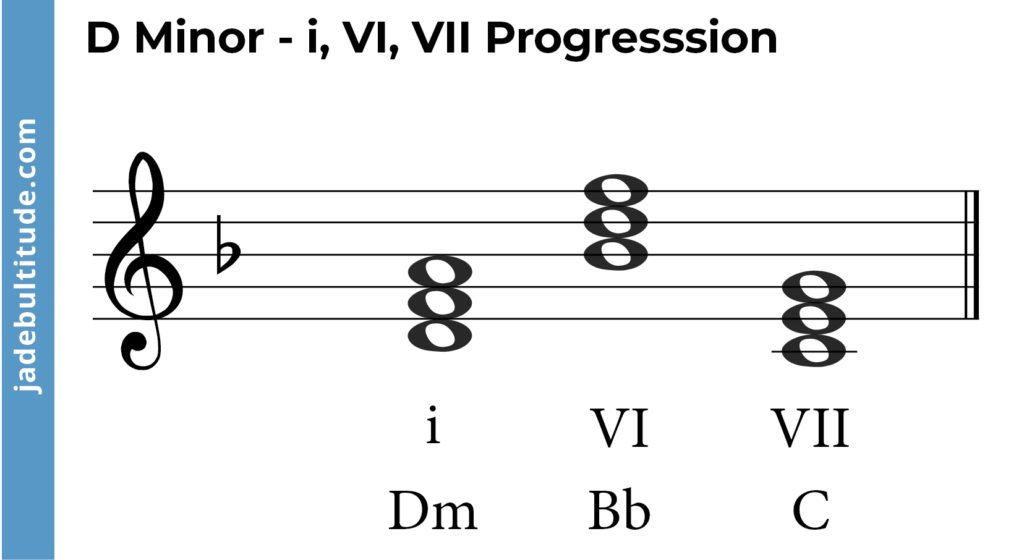
Chord Progressions in D Minor
- i – VI – VII (Dm – Bb – C)
- i – iv – VII (Dm – Gm – C)
- i – iv – v (Dm – Gm – Am)
- i – VI – III – VII (Dm – Bb – F – C)
- ii – v – I (Em7b5 – Am – Dm)

Ear Training and Chords
To develop as a musician you’ll want to be able to recognise chords by ear. This is where ear training comes in. My recommendation for this is Tonegym as they have a comprehensive and fun program for training your ears! It’s what has gotten the best results with for my own students.
In the ‘tools’ section of their site, Tonegym even have a chord player that allows you to listen virtually any chord.
For an in-depth look at ear training, here’s my full review of Tonegym.
Piano Chords in D Minor
If you are interested in playing the piano version of these chords then below are diagrams for all chords in D minor.
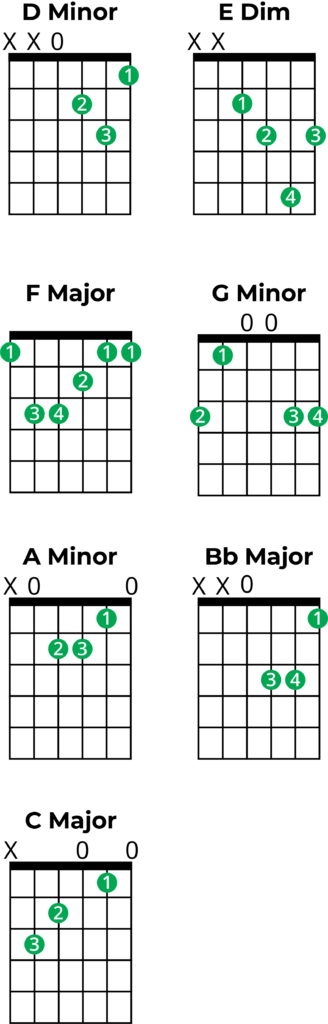
Guitar Chords in D Minor
Here are the guitar charts for chords in D minor. The numbers inside the green circle show a suggested fingering for each chord.
Chord Inversions
There are different versions of these chords that we could play called ‘inversions’. To invert a chord means to change the order of the notes by having the 3rd, 5th or 7th note as the lowest note in pitch. For more on chord inversions on this see our complete guide to chords.
What should I learn next?
- The relative major of D Minor is F major. The relative major key means that it has the same key signature (one flat- Bb) but the scale starts and ends on F natural. Learn about chords in F Major.
- Learn more about chords with our complete guide
- Learn about a different scale or key signature.
